Current Ratio Explained With Formula and Examples
Set a quick ratio benchmark that aligns with industry standards to ensure your business is well-positioned for stability and growth. The quick ratio may also be more appropriate for industries where inventory faces obsolescence. In fast-moving industries, a company’s warehouse of goods may quickly lose demand with consumers. In these cases, the company may not have had the chance to reduce the value of its inventory via a write-off, overstating what it thinks it may receive due to outdated market expectations. The available research on day trading suggests that most active traders lose money.
How to calculate the quick ratio
A high ratio implies that the company has a thick liquidity cushion. Over-trading companies are likely to face substantial difficulties in meeting their day-to-day obligations. The current ratio can be expressed in any of the following three ways, but the most popular approach is to express it as a number.
Which of these is most important for your financial advisor to have?
Here’s a look at both ratios, how to calculate them, and their key differences. I teach so traders like you can have the opportunity an make a better future. And if you thought that was easy, try using the StocksToTrade software.
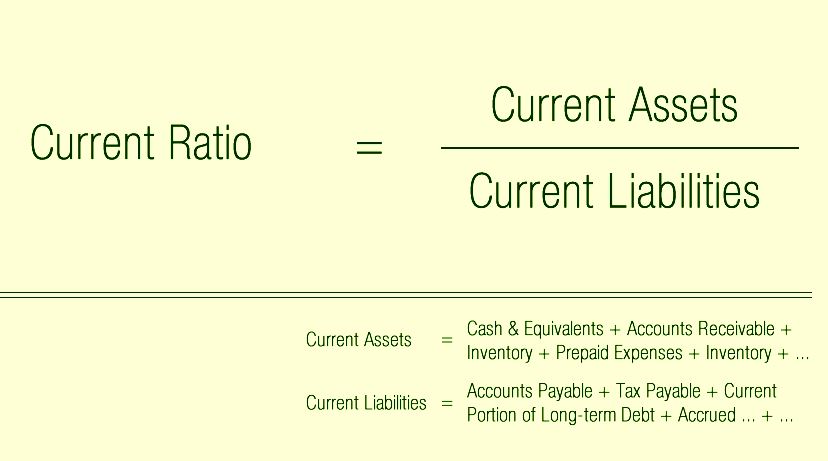
- You can find them on your company’s balance sheet, alongside all of your other liabilities.
- Current liabilities include accounts payable, wages, accrued expenses, accrued interest and short-term debt.
- The current ratio expressed as a percentage is arrived at by showing the current assets of a company as a percentage of its current liabilities.
- This article and related content is not a substitute for the guidance of a lawyer (and especially for questions related to GDPR), tax, or compliance professional.
Ask the author a question or share your advice
This team of experts helps Finance Strategists maintain the highest level of accuracy and professionalism possible. At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content. Current assets refers to the sum of all assets that will be used or turned to cash in the next year. Get instant access to video lessons taught by experienced investment bankers. Learn financial statement modeling, DCF, M&A, LBO, Comps and Excel shortcuts.
Besides, you should analyze the stock’s Sortino ratio and verify if it has an acceptable risk/reward profile. If you are interested in corporate finance, you may also try our other useful calculators. Particularly interesting may be the return on equity calculator and the return on assets calculator. Current liabilities are obligations that are to be settled within 1 year or the normal operating cycle. So, a ratio of 2.65 means that Sample Limited has more than enough cash to meet its immediate obligations. A financial professional will be in touch to help you shortly.
I was sick of using so many websites to find the information I needed. StocksToTrade has everything you need in one place, even ratios. But 99% of these companies likely won’t even exist in a few years. I often stress to my students to prepare before you risk your hard-earned money. Too many people are too lazy in this industry to put in the work to be successful.
The Current Ratio provides valuable insights into a company’s liquidity. It’s particularly useful when assessing the short-term financial health of potential investment opportunities. This ratio, however, should not be viewed in isolation but rather square + xero as part of a holistic financial analysis. In the dynamic world of finance, it’s essential to navigate the complexities of financial ratios. Today, we unravel the ‘Current Ratio,’ a key metric used to assess a company’s financial health.
As a general rule of thumb, a current ratio in the range of 1.5 to 3.0 is considered healthy. The offers that appear on this site are from companies that compensate us. But this compensation does not influence the information we publish, or the reviews that you see on this site. We do not include the universe of companies or financial offers that may be available to you. Professional services firms rely on accounts receivable rather than inventory. This ratio reflects your business’s capacity to cover expenses, pay employees, and make necessary investments without delay.
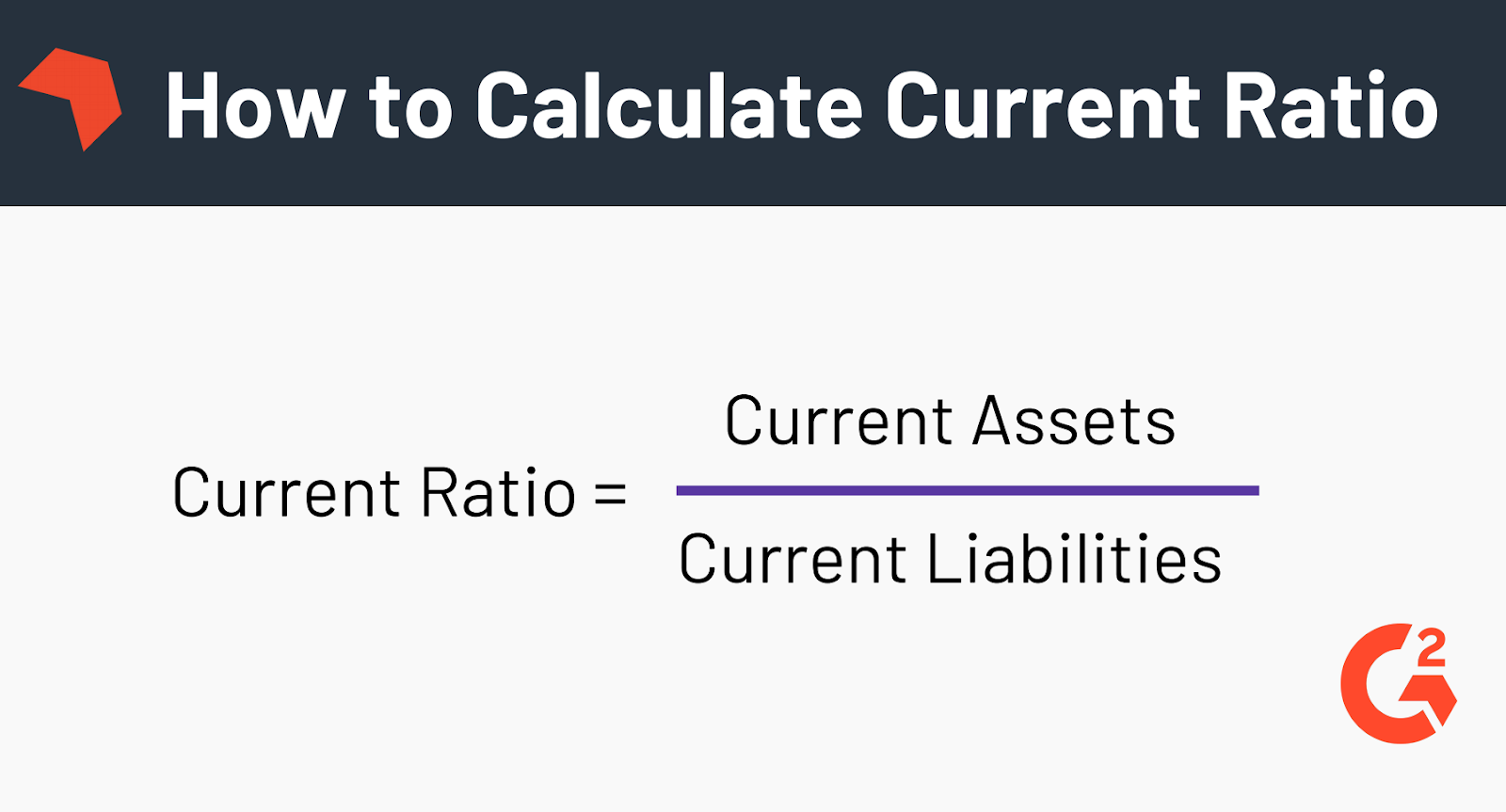
Although they’re both measures of a company’s financial health, they’re slightly different. The quick ratio is considered more conservative than the current ratio because its calculation factors in fewer items. Since the current ratio compares a company’s current assets to its current liabilities, the required inputs can be found on the balance sheet. The formula to calculate the current ratio divides a company’s current assets by its current liabilities. Investors can use this type of liquidity ratio to make comparisons with a company’s peers and competitors.
Here, the company could withstand a liquidity shortfall if providers of debt financing see the core operations are intact and still capable of generating consistent cash flows at high margins. The range used to gauge the financial health of a company using the current ratio metric varies on the specific industry. For the last step, we’ll divide the current assets by the current liabilities. To see how current ratio can change over time, and why a temporarily lower current ratio might not bother investors or analysts, let’s look at the balance sheet for Apple Inc. Though they may appear to have the same level of risk, analysts would have different expectations for each company depending on how the current ratio of each had changed over time. Internally, you can use the quick ratio to assess liquidity, plan future expenditures, and identify opportunities to enhance cash flow.
